Using the correct tool for the job and optimizing scanner placement will have a large impact on scan efficiency with Nessus, Tenable.io and Tenable.sc.
When working with Nessus at scale or in unique environments, it can be a challenge to balance scan time, target resource usage and assessment effectiveness. In this blog post, we’ll cover some common configurations that you can use to optimize scan times and reduce load on scan targets and network infrastructure.
The first item to consider is the appropriate scan or assessment method for your target and your objective. Different types of systems require different methods of assessment. And there are different goals when doing a host or network scan, including::
- Scan a large network and see what hosts are on it.
- Assess remote user workstations for vulnerabilities.
- Review the configuration of Apache against a security baseline.
- Ensure that a sensitive network doesn’t have systems added to it outside of change control.
Each of these scenarios could use the same basic configuration, but as every IT environment is unique, understanding the way to optimize each will make your program more effective.
Assessment goals
What is your objective? Using the examples above, let’s take a look at ways to be more efficient than with a generic network scan, depending on what you’re trying to accomplish.
- Nessus uses a variety of methods to determine if a host is alive. These are performed in a specific order so that systems are detected as quickly as possible. However if you know that a certain discovery method isn’t applicable to your environment, you can disable it.
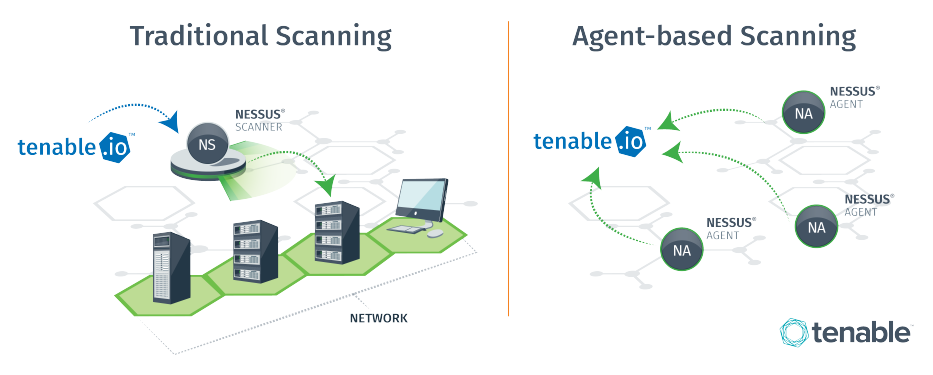
- Remote workstations are often very hard to reach via traditional network methods. Installing a local Nessus Agent will enable local assessment of the host and upload of the data back for centralized reporting. Meanwhile, attempting to assess over a VPN or wireless connection can result in dropped packets, corrupted scans and performance impacts on network infrastructure.
![Tuning Network Assessments for Performance and Resource Usage -- image #1]()
- Compliance benchmarks require authentication and perform validation against local configuration settings. If you’re only running compliance checks, you can use a specific scan policy to ensure that only the configurations required are enabled and that un-necessary checks are not performed.
- In general, systems in sensitive environments should not be network-scanned using traditional IT methods. While Nessus will attempt to avoid these systems during a scan, agents or passive assessments of these hosts are generally safer and can still provide valuable information without impacting the availability of the specialized assets.
In summary, the first step is to ensure you’re using the correct tool and configuration for the job.
Simultaneous assessment
When exploring the most effective way to perform an assessment, scanning many systems simultaneously isn’t always the best option. Just because the tool is capable of a certain threshold doesn’t mean it should be maxed out. Consider the following:
- If network traffic from your scan passes through a single bottleneck, that network infrastructure may be overwhelmed by the number of hosts being assessed at any given moment.
- Scans on hosts sharing the same underlying infrastructure, such as storage or compute resources, may overwhelm those systems if too many assessments start at the same time.
- Some checks will query other local or internet infrastructure as part of the assessment. This can overwhelm infrastructure with additional connections or queries the systems that aren’t being explicitly assessed.
The default scan configurations for simultaneous assessments of scan targets is sufficient for most use cases. However, this may be scaled up to increase performance or scaled down to reduce impact on infrastructure. There are other options within the scan configurations to address specific issues, such as:
- Stagger scan launch times for Nessus Agents
- Randomize the order in which IPs are scanned
- Slow down the scan when network congestion is detected
Scanner resources and placement
In general, Nessus sensors should meet the recommended hardware requirements whenever possible. This allows Nessus to scale appropriately to most network sizes and run a large variety of assessments at once.
Occasionally, you may not have dedicated hardware or resources that meet even the minimum Nessus specs. In these cases, you can use shared resources to a certain extent, assuming that you keep in mind expectations on reduced functionality. A shared Windows server in an office trailer with 10 systems will likely be sufficient to install Nessus on (and only scan those 10 targets), and generally makes more sense than setting up an entirely new system dedicated to Nessus.

You should also deploy scanners as close as possible to the targets being assessed. For example, a regionally distributed network with 25 distinct Class B subnets may benefit from a scanner in each one, if there is no centralized (or robust) backbone to a central hub. A scanner that’s as close as possible to the targets will achieve various goals like:
- Using ARP if it’s in the same subnet as the targets
- Reduced or no load on infrastructure to scan through
- Quicker scans due to reduced network transit time
However, this is not always possible, nor optimal, in every environment. In the scenario above, perhaps there is no infrastructure at each network, and creating such an infrastructure is cost prohibitive. In this case, deploying other types of technologies (Nessus Agents, Nessus on a Raspberry Pi, Nessus Network Monitor, etc) may achieve the same end goal.
Enterprise platform configuration
One of the fastest ways to improve scan times is to simply increase the number of scanners you’re using. With Tenable Enterprise platforms like Tenable.io or Tenable.sc, customers can deploy as many scanners as they wish, allowing for complex network configurations deployments.
Customers can also logically group scanners in both Tenable.io and Tenable.sc (using Scanner Groups and Scan Zones, respectively) so that one scan task is broken out over many scanners. This effectively increases the concurrent hosts tested at any given time while reducing the potential bottleneck around scanner resources.
Be aware however that increasing the number of scanners will also increase the amount of network traffic and connections made to endpoints. This can overwhelm network infrastructure if scanners are improperly placed or additional configurations are made to the scan policies. Tenable recommends monitoring network usage and coordinating changes with internal infrastructure teams to ensure there is no impact to production networks.
Making your network assessments as efficient as possible will depend on a number of factors. In this article, we’ve covered the basics of planning out your goals for assessment, checking numerous hosts at the same time, scanner placement and resource usage, and utilizing Tenable.io and Tenable.sc’s capabilities around multiple scanners.
Learn more:
- Nessus Discovery Settings (Documentation)
- Nessus Scanner Hardware Requirements (Documentation)
- Advanced Settings in Vulnerability Management Scans - Tenable.io (Documentation)
- Variables Impacting Scan Time (Documentation)
- Scanner Groups - Tenable.io (Documentation)
- Scan Zones - Tenable.sc (Documentation)
- 4 Ways to Improve Nessus Scans Through Firewalls (Blog)
- Configuring the Ports that Nessus Scans (Blog)
- ICS/SCADA Smart Scanning (Blog)