Frequently asked questions about CVE-2024-3094, a supply-chain attack responsible for a backdoor in XZ Utils, a widely used library found in multiple Linux distributions.
Update March 29: The "What Linux distributions are affected?" section has been updated to include additional affected and not affected distributions and a note about the Homebrew package manager.
Background
The Tenable Security Response Team has put together this blog to answer Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) regarding CVE-2024-3094, a backdoor in XZ Utils, a widely used compression library found in multiple Linux distributions.
FAQ
What is XZ Utils and what is the library used for?
XZ is a type of lossless data compression on Unix-like operating systems, which is often compared to other common data compression formats such as gzip and bzip2. XZ Utils is a command line tool that contains functionality for both compression and decompression of XZ files and liblzma, a zlib-like API used for data compression and also supports the legacy .lzma format.
How was this backdoor discovered?
On March 29, Andres Freund, a PostgreSQL developer at Microsoft, posted on the Open Source Security Mailing List that he had discovered a supply-chain compromise involving obfuscated malicious code in the XZ package while investigating SSH performance issues. According to both Freund and RedHat, the malicious code is not present in the Git distribution for XZ and only in the full download package.
Which versions of the library are affected?
According to Freund, XZ Utils versions 5.6.0 and 5.6.1 are impacted.
Has this backdoor code been exploited?
No information regarding exploitation has been observed for this backdoor code as of March 29. Because this situation is still developing, we anticipate more information will come to light in the coming days and weeks. We will update this portion of the FAQ once such information is available.
What is the impact of this backdoor?
According to Red Hat, the malicious code modifies functions within the liblzma code, which is part of the XZ Utils package. This modified code can then be used by any software linked to the XZ library and allow for the interception and modification of data used with the library. In the example observed by Freund, under certain conditions, this backdoor could allow a malicious actor to “break sshd authentication,” allowing the attacker to gain access to an affected system.
Is there a CVE assigned for this issue?
Yes, Red Hat assigned CVE-2024-3094 for this issue and it has been given a CVSSv3 score of 10.0.
How was this backdoor inserted into the code?
At the time this blog was published, it’s unclear how this backdoor code was placed into the affected builds of XZ utils. According to Freund, it's likely the individual who made the code commits is directly involved with the XZ project or had their system or developer account compromised.
What Linux distributions are affected?
As of the time this blog was published on March 29, the following distributions are known to be affected:
| Distribution | Advisory | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Fedora Rawhide | https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/urgent-security-alert-fedora-41-and-rawhide-users | Fedora Rawhide is the development distribution of Fedora Linux |
| Fedora 41 | https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/urgent-security-alert-fedora-41-and-rawhide-users | |
| Debian testing, unstable and experimental distributions versions 5.5.1alpha-0.1 to 5.6.1-1. | https://lists.debian.org/debian-security-announce/2024/msg00057.html | |
| openSUSE Tumbleweed and openSUSE MicroOS | https://news.opensuse.org/2024/03/29/xz-backdoor/ | Backdoored version of xz was included in Tumbelweed and MicroOS between March 7 and March 28 |
| Kali Linux | https://www.kali.org/blog/about-the-xz-backdoor/ | Backdoored version of xz was included in Kali Linux (xz-utils 5.6.0-0.2) between March 26 and March 28 |
The following Linux distributions are confirmed to not be affected:
| Distribution | Advisory | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Fedora Linux 40 | https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/urgent-security-alert-fedora-41-and-rawhide-users | RedHat recommends that users downgrade to a 5.4 build of XZ as a precaution |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) | https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/urgent-security-alert-fedora-41-and-rawhide-users | No versions of RHEL are affected. |
| Debian | https://lists.debian.org/debian-security-announce/2024/msg00057.html | No Debian stable versions are known to be affected. |
| Amazon Linux | https://aws.amazon.com/security/security-bulletins/AWS-2024-002/ | Amazon Linux customers are not affected and AWS Infrastructure and services do not utilize xz. |
| SUSE Linux Enterprise and Leap | https://news.opensuse.org/2024/03/29/xz-backdoor/ | Both Enterprise and Leap are isolated from OpenSUSE and are unaffected. |
Additionally, the macOS Homebrew package manager reverted its version of xz from 5.6.x to 5.4.6. Bo Anderson, a member of the technical steering committee and a maintainer of Homebrew, confirmed that they do not believe Homebrew’s builds “were compromised” but because these versions of xz are not considered trustworthy, they have chosen to force downgrades “as a precaution.”
As this is a developing situation, we anticipate we will have further clarity for additional Linux distributions soon and will continue to update this blog as necessary.
Are patches or mitigations available?
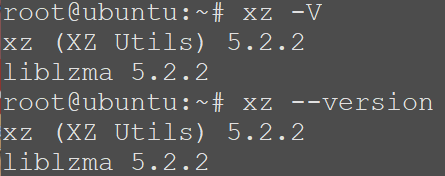
Both developers and users of XZ Utils are advised to downgrade to known, unaffected versions of XZ Utils, such as 5.4.6 Stable. However, in addition to downgrading, it is strongly advised that developers and users conduct incident response to determine if they have been impacted as a result of this backdoor and to share “positive findings” with agencies like the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA). You can check your installed version by running the command ‘xz -V’ or ‘xz –version’.
Has Tenable released any product coverage for these vulnerabilities?
As of March 29, Tenable Research is investigating product coverage. A list of Tenable plugins for this vulnerability can be found on the individual CVE page for CVE-2024-3094 as they’re released. This link will display all available plugins for this vulnerability, including upcoming plugins in our Plugins Pipeline.
Change Log
Update March 29: The "What Linux distributions are affected?" section has been updated to include additional affected and not affected distributions and a note about the Homebrew package manager.
Get more information
- Open Source Security Mailing List post by Andres Freund
- Red Hat: Urgent security alert for Fedora Linux 40 and Fedora Rawhide users
- Debian: xz-utils security update
- CISA Alert: Reported Supply Chain Compromise Affecting XZ Utils Data Compression Library, CVE-2024-3094
Join Tenable's Security Response Team on the Tenable Community.
Learn more about Tenable One, the Exposure Management Platform for the modern attack surface.
