Vulnerability assessments and vulnerability management sound similar – but they’re not. As a new Enterprise Strategy Group white paper explains, it’s key to understand their differences and to shift from ad-hoc vulnerability assessments to continuous, risk-based vulnerability management (RBVM). Read on to check out highlights from this Tenable-commissioned study and learn how RBVM helps organizations attain a solid security and risk posture in hybrid, complex and multi-cloud environments.
Don’t conflate vulnerability assessments with vulnerability management.
To effectively manage security risks, you need continuous and comprehensive vulnerability management – not just point-in-time vulnerability assessments conducted periodically or on an ad-hoc basis. While vulnerability assessments are important, they are only part of a broader vulnerability management program for reducing risks and boosting the security posture of modern IT environments.
This is the focus of a new Enterprise Strategy Group (ESG) white paper commissioned by Tenable and titled “Elevating Security with Risk-based Vulnerability Management.” The report details why you need a risk-based vulnerability management (RBVM) program that not only assesses vulnerabilities, but also involves prioritizing, taking action, reassessing and incorporating improvements. In this blog post, we’ll dig into some of the key takeaways from the report.
What are vulnerability assessments and their limitations?
ESG defines vulnerability assessments as “point-in-time network scans used to discover IT assets, applications, and their associated vulnerabilities.” By relying on these periodic assessments, organizations struggle to fully track and measure the success of their program. They often can’t answer important questions like:
- “Did we scan 100% of the assets in the environment?”
- “Did we address all critical vulnerabilities in a timely manner?”
- “Are we reducing our overall risk?”
Without answers to questions like these, organizations can’t determine the long-term impact of their efforts.
With the adoption of cloud services, IoT devices, operational technology (OT) systems, mobile endpoints and more, organizations must manage and secure highly complex hybrid, multi-cloud environments. Given that vulnerability assessment tools are designed to scan one IT environment at a time, organizations relying on such legacy tools often must conduct multiple individual scans to cover their environments. Even then, full asset visibility is still a challenge with legacy tools that aren’t designed to detect and secure modern assets like virtual machines, containers, cloud infrastructure and ephemeral workloads.
Scan results must then be aggregated into a single location for prioritization and remediation efforts. Legacy vulnerability assessment tools struggle when it comes to workflow automation, which can be quite costly for organizations. As stated in the ESG white paper: “Legacy tools themselves may be cheaper, but the additional human hours required to drive productive action out of the findings end up being more expensive than the software savings.”
Biggest vulnerability management program challenges
According to ESG’s survey of 383 IT and cybersecurity professionals, the top 3 challenges that organizations face with their current vulnerability management processes and tools are:
- Automating processes such as vulnerability discovery, prioritization and mitigation
- Tracking vulnerabilities that lack patches or that can’t be patched
- Struggling to coordinate vulnerability management processes across different tools
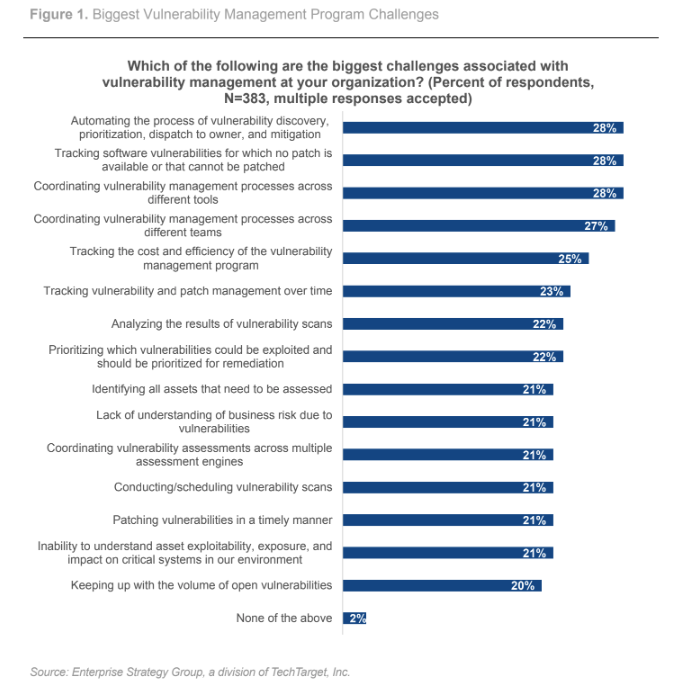
This data showcases the need for a vulnerability management solution that goes beyond legacy vulnerability assessment to provide strong workflow automation capabilities, effective and efficient risk-based prioritization, and a means to bridge the gap between security and remediation teams.
The benefits of continuous, risk-based vulnerability management
Adopting a continuous, risk-based vulnerability management program is critical for more effective risk reduction and for an enhanced security posture.
To adopt a risk-based approach to vulnerability management, ESG highlights three key elements needed to contextualize vulnerabilities and prioritize risk effectively and efficiently:
- Impact: If a vulnerability were to be successfully exploited, you need to understand the impact to the affected asset and to the organization overall.
- Likelihood of exploitation: Understanding which vulnerabilities are being actively exploited in the wild and which vulnerabilities can be easily exploited is an important factor in your prioritization efforts.
- Asset value: This factor has become more complex in recent years, as asset value is no longer just about determining which systems are running critical software. Asset value is also about identity data, and the roles and permissions granted to users of a system.
Maturing your organization’s vulnerability management program into a proactive, comprehensive program for effective risk reduction will better enable you to meet the needs of modern workloads. To dig deeper into ESG’s findings, download the full white paper today.
How Tenable Vulnerability Management can help
Tenable Vulnerability Management is a risk-based vulnerability management platform that brings an effective, modern approach to solving today’s toughest vulnerability management challenges.
Managed in the cloud and powered by Tenable Nessus, Tenable Vulnerability Management provides the industry’s most comprehensive vulnerability coverage with real-time continuous assessment of organizations and full ecosystem visibility to predict attacks and quickly respond to critical vulnerabilities.
To learn more about Tenable Vulnerability Management, start your free trial todayand download the white paper “Elevating Security with Risk-based Vulnerability Management.”
