IBM’s latest “Cost of a Data Breach Report” finds these data-theft incidents getting more expensive. Plus, the IT-ISAC says that ransomware attacks fell in Q2 due to law-enforcement disruptions of ransomware groups. Meanwhile, check out a Carnegie Mellon comp sci professor’s take on AI system security. And Tenable’s headed to Black Hat – visit our booth! And much more!
Dive into six things that are top of mind for the week ending August 2.
1 - IBM: Data breach costs up 10% to almost $5 million
A data breach now costs organizations an average of $4.88 million, a jump of 10% from last year that was driven by the cost of lost business and by incident response expenses, according to IBM’s “Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024,” which was published this week.
And breaches created substantial turmoil: For 70% of the organizations surveyed, data breaches caused either a “significant” or “very significant” disruption to their business. “Business runs on data. When data is breached, business is disrupted,” the report reads.
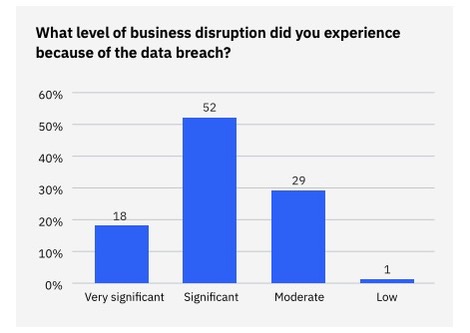
(Source: IBM’s “Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024,” July 2024)
Meanwhile, AI has become both a blessing and a curse, helping security teams and data thieves alike.
Security teams that use AI and automation extensively for prevention experience an average of $2.2 million less in breach costs than security teams that don’t use AI at all. Two-thirds of organizations surveyed are using AI and automation for cybersecurity.
“AI and automation solutions are reducing the lifespan needed to identify and contain a breach and its resulting damage,” reads the report, which is based on an analysis of data breaches experienced by 604 organizations globally.
On the other hand, as organizations adopt generative AI aggressively, they’re expanding their attack surface, creating “unprecedented risks” and increasing the pressure on security teams.
Here are other key findings from the report, whose research was conducted by Ponemon Institute and sponsored and analyzed by IBM:
- More than half of the surveyed organizations face “high levels” of security understaffing, a 26.2% percent increase from last year. These organizations experienced an average of $1.7 million more in breach costs than organizations that are either fully staffed or that have a low understaffing level.
- 35% of breaches involved “shadow data,” which the report describes as data that’s stored in unmanaged data sources and is thus harder to track and protect.
- Organizations that tapped law enforcement after suffering a ransomware attack lowered the average cost of a data breach by $1 million, excluding ransom costs.
- Attacks involving stolen credentials took the longest to identify and contain – 292 days.
- The factor that has the greatest impact on reducing data breach costs is employee training. Meanwhile, the factor that most increases data-breach costs is security system complexity.
To get more details:
- Read the report’s announcement “IBM Report: Escalating Data Breach Disruption Pushes Costs to New Highs”
- Download the “Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024.”
For more information about preventing data breaches:
- “Why data breaches have become ‘normalized’ and 6 things CISOs can do to prevent them” (VentureBeat)
- “How to prevent a data breach: 10 best practices and tactics” (TechTarget)
- “Data breaches are increasing at a rapid speed. Here’s what can be done” (World Economic Forum)
- “8 data protection challenges and how to prevent them” (TechTarget)
2 - IT-ISAC: Ransomware attacks down in Q2
Ransomware attacks observed by the Information Technology-Information Sharing and Analysis Center (IT-ISAC) dropped 21% during the second quarter, compared with the first quarter, a decrease driven by recent law-enforcement disruptions of ransomware groups.
And in yet another reminder to keep software patched and updated, the exploitation of known vulnerabilities ranked as the top initial-access vector for ransomware attacks in the second quarter.
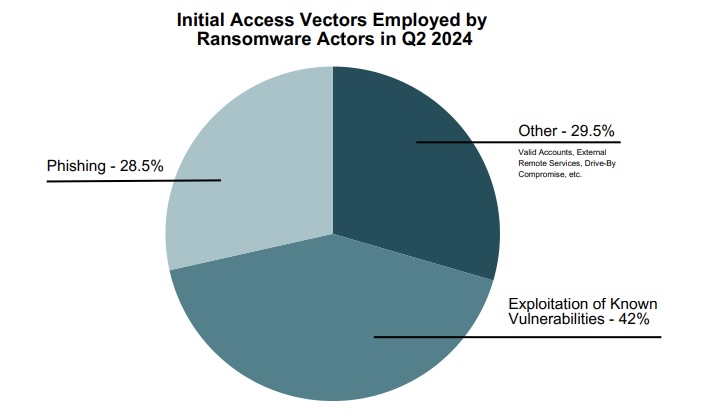
(Source: IT-ISAC’s “Exploring the Depths: An Analysis of the 2023 Ransomware Landscape and Insights for 2024” report, updated in July 2024)
Some of the vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware attackers in the second quarter included CVE-2020-1472, CVE-2023-22518, CVE-2024-26169 and CVE-2024-4577, IT-ISAC said in its report “Exploring the Depths: An Analysis of the 2023 Ransomware Landscape and Insights for 2024,” which was updated in July 2024.
Meanwhile, critical manufacturing, commercial facilities and healthcare were the three sectors that suffered the most attacks, collectively accounting for 47.6% of attacks, while the IT sector was hit by almost 7%.
To get more details, read the full report “Exploring the Depths: An Analysis of the 2023 Ransomware Landscape and Insights for 2024.”
For more information about ransomware prevention:
- “Steps to Help Prevent & Limit the Impact of Ransomware” (Center for Internet Security)
- “How Can I Protect Against Ransomware?” (CISA)
- “Mitigating malware and ransomware attacks” (U.K. National Cyber Security Centre)
- “Ransomware: How to prevent and recover” (Canadian Centre for Cyber Security)
3 - Visit Tenable at Black Hat
Are you attending Black Hat USA 2024 in Las Vegas next week? As usual, Tenable will be participating and we’d love to see you at our booth (#1932) where we’ll have exciting product demos, lightning talks, cool swag and much more.

You can also find us at the Tenable Research Lounge (Breakers K, Level 2) on August 7 and 8.
And don’t miss these presentations from Tenable experts:
Speaker: Sean Jennings, Principal Enterprise Security Engineer
Wednesday, August 7 at 11:25 am
Location: Business Hall Theater C
Speaker: Liv Matan, Senior Research Engineer
Wednesday, August 7 at 1:30 pm
Location: South Pacific F, Level 0
4 - Carnegie Mellon prof. outlines AI security challenges
If you want to learn more about securing AI systems, you might be interested in reading a new blog from a Carnegie Mellon University professor titled “Weaknesses and Vulnerabilities in Modern AI: Why Security and Safety Are so Challenging.”
In the blog, author Bill Scherlis, a CMU computer science professor and former director of DARPA’s Information Innovation Office, explains that modern AI-based systems have their own set of weaknesses and vulnerabilities that create risks that are particular to them. As such, these risks must be taken into account when designing and evaluating AI-based systems.
“In the excitement to create systems that build on modern AI, including neural-network-based machine learning (ML) and generative AI models, it is easy to overlook the weaknesses and vulnerabilities that make these models susceptible to misdirection, confidentiality breaches, and other kinds of failures,” Scherlis wrote.
In his blog, the first of a four-part series, Scherlis aims to identify the following:
- The appropriate concepts of security and safety for modern neural-network-based AI, including ML and generative AI, such as LLMs
- The AI-specific challenges involved in developing safe and secure systems
- Modern AI’s trustworthiness limits, and why these limits are fundamental
For more information about securing AI systems:
- “OWASP AI Security and Privacy Guide” (OWASP)
- “Deploying AI Systems Securely” (Australian Cyber Security Centre)
- “Guidelines for secure AI system development” (U.K. National Cyber Security Centre)
- “How to secure AI system development” (VentureBeat)
5 - An Tenable poll on cloud security
During our recent webinar “Tenable Cloud Security Outlook 2024,” we polled attendees about their cloud security practices. Check out what they said about production cloud workloads and about cloud remediation.
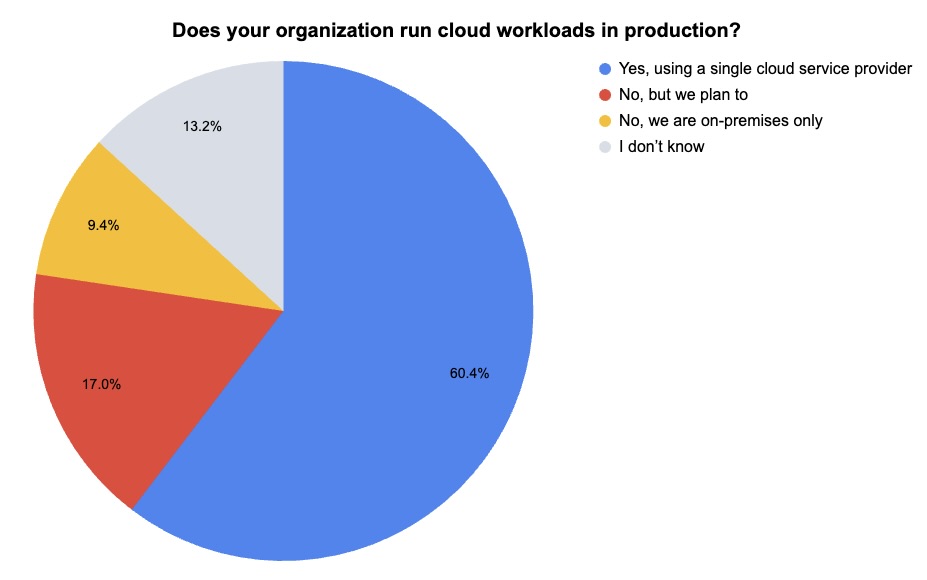
(53 webinar attendees polled by Tenable, July 2024)
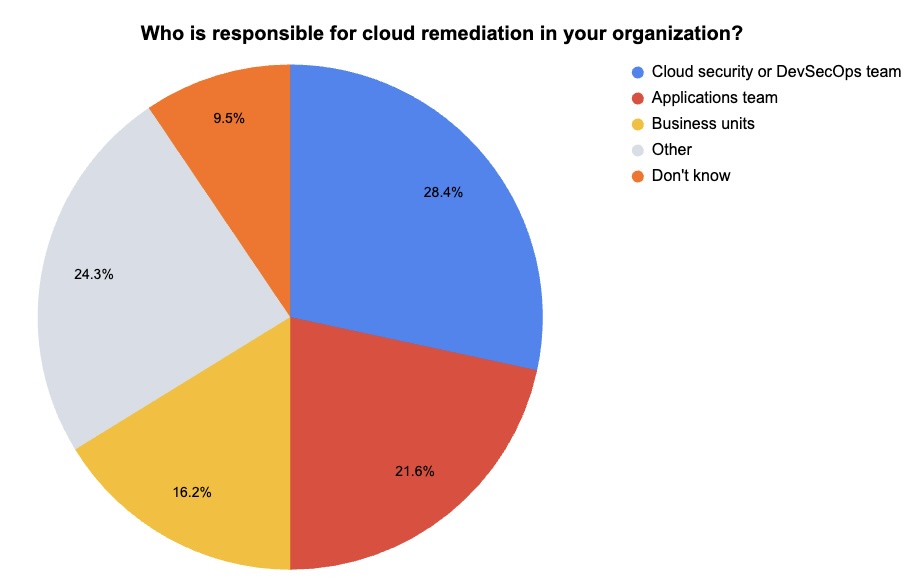
(74 webinar attendees polled by Tenable, July 2024)
If you missed it, you can watch this webinar on-demand and get the details from our global “2024 Cloud Security Outlook” study, learn about data-breach prevention strategies and more.
6 - CISA appoints its first AI chief
And in a clear sign of the times, the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has selected its first ever head of AI.
This week, CISA announced that Lisa Einstein has been appointed as its Chief Artificial Intelligence Officer, after leading the agency’s AI efforts since 2023 as Senior Advisor for AI.
“This selection reflects CISA’s commitment to responsibly use AI to advance its cyber defense mission and to support critical infrastructure owners and operators across the United States in the safe and secure development and adoption of AI,” reads a CISA statement.
